Segregated Temporal Assembly Recurrent Networks for Weakly Supervised Multiple Action Detection
Abstract
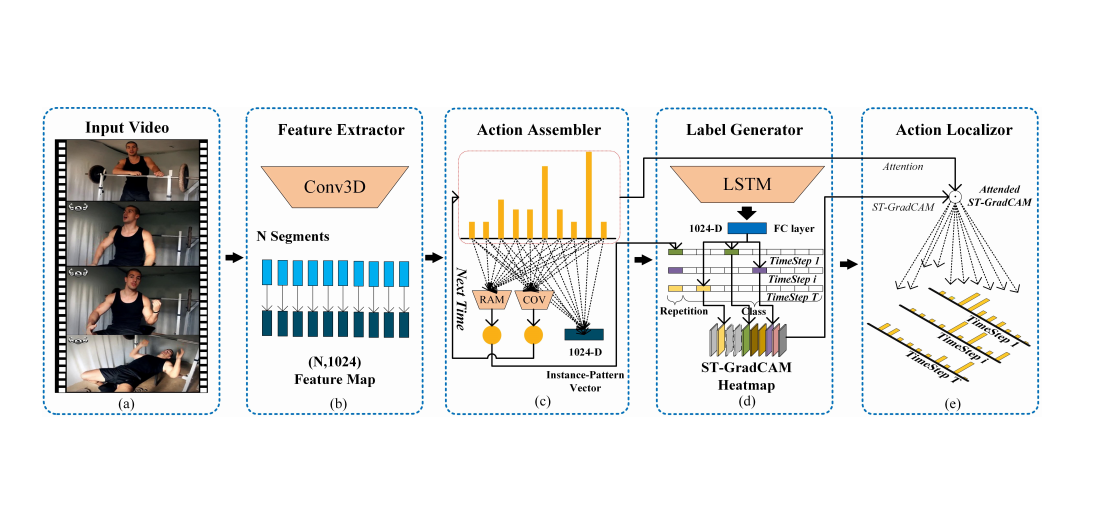
Video text spotting is still an important research topic due to its various real-applications. This paper proposes a segregated temporal assembly recurrent (STAR) network for weakly-supervised multiple action detection. The model learns from untrimmed videos with only supervision of video-level labels and makes prediction of intervals of multiple actions. Specifically, we first assemble video clips according to class labels by an attention mechanism that learns class-variable attention weights and thus helps the noise relieving from background or other actions. Secondly, we build temporal relationship between actions by feeding the assembled features into an enhanced recurrent neural network. Finally, we transform the output of recurrent neural network into the corresponding action distribution. In order to generate more precise temporal proposals, we design a score term called segregated temporal gradient-weighted class activation mapping (ST-GradCAM) fused with attention weights. Experiments on THUMOS’14 and ActivityNet1.3 datasets show that our approach outperforms the state-of-the-art weakly-supervised method, and performs at par with the fully-supervised counterparts. [Paper]Highlights Contributions
❃ We reformulate the multiple action detection from a multi-instance multi-label (MIML) perspective, i.e., extracting instance-patterns and generating action labels, which eliminates interference among unrelated action features and captures temporal dependency between multiple concurrent actions.
❃ We propose an end-to-end framework called Segregated Temporal Assembly Recurrent (STAR), which includes a well-designed attention module and an enhanced RNN, is developed to be trained in a weakly supervised manner from videos with only video-level labels.
❃ We design an ST-GradCAM operation fused with class-variable assembly weights for action temporal localization.
❃ Our extensive experiments demonstrate that our weakly supervised framework achieves impressive performance on the challenging THUMOS'14 and ActivityNet1.3 datasets for action detection, comparable with those of supervised learning methods.
Recommended Citations
If you find our work is helpful to your research, please feel free to cite us:
@inproceedings{xu2019segregated,
title={Segregated temporal assembly recurrent networks for weakly supervised multiple action detection},
author={Xu, Yunlu and Zhang, Chengwei and Cheng, Zhanzhan and Xie, Jianwen and Niu, Yi and Pu, Shiliang and Wu, Fei},
booktitle={Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence},
volume={33},
pages={9070--9078},
year={2019}
}