Reciprocal Feature Learning via Explicit and Implicit Tasks in Scene Text Recognition
Abstract
Text recognition is a popular topic in recent years for its broad applications. In this work, we excavate the implicit task, character counting within the traditional text recognition, without additional labor annotation cost. The implicit task plays as an auxiliary branch for complementing the sequential recognition. We design a two-branch reciprocal feature learning framework in order to adequately utilize the features from both the tasks. Through exploiting the complementary effect between explicit and implicit tasks, the feature is reliably enhanced. Extensive experiments on 7 benchmarks show the advantages of the proposed methods in both text recognition and the new-built character counting tasks. In addition, it is convenient yet effective to equip with variable networks and tasks. We offer abundant ablation studies, generalizing experiments with deeper understanding on the tasks. Code is available. [Paper]Highlights Contributions
❃ We propose a unified framework VSR for document layout analysis, combin- ing vision, semantics and relations.
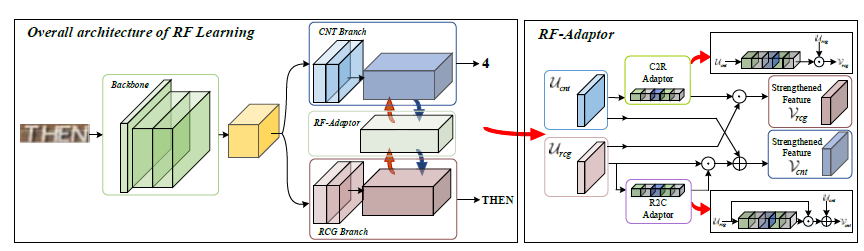
❃ We dig the implicit task in the traditional STR, i.e., character counting, without any extra annotation cost. The counting network supervised by new ex- ploited labels can be regarded as an auxiliary part in addition to the recognition task, facilitating positive outcomes. Also, we offer a strong baseline for the sole newly-built character counting task based on the existing STR datasets.
❃ We propose a multi-task learning framework called RF-L for STR through exploiting the complementary effect between two different tasks, word recogni- tion and counting respectively. And the two tasks are learned in their own branch, in interaction to the other, via a simple yet effective RF-Adaptor module.
❃ The proposed method achieves impressive improvements in multiple bench- marks, not only in STR tasks but also in counting. The auxiliary network and the adaptor can be easily integrated into deep neural network with any other scene text recognition method, which boosts the single task via the proposed RF-L framework as verified in extensive experiments.
Recommended Citations
If you find our work is helpful to your research, please feel free to cite us:
@inproceedings{jiang2021Reciprocal,
title={Reciprocal Feature Learning via Explicit and Implicit Tasks in Scene Text Recognition},
author={Jiang, Hui and Xu, Yunlu and Cheng, Zhanzhan and Pu, Shiliang and Niu, Yi and Ren, Wenqi and Wu, Fei and Tan, Wenming},
booktitle = {ICDAR},
volume= {12821},
pages= {287--303},
year={2021},
}